Definition Of X Ray Diffraction
X-ray diffraction - the scattering of X rays by the atoms of a crystal. Introduction to Crystallography and X-Ray Diffraction Theory Diffraction occurs when light is scattered by a periodic array with long-range order producing constructive interference at specific angles.
 X Ray Diffraction Xrd Ppt Download
X Ray Diffraction Xrd Ppt Download
It provides information on structures phases preferred crystal orientations texture and other structural parameters such as average grain size crystallinity strain and crystal defects.

Definition of x ray diffraction. It is non-destructive and works most effectively with materials that are wholly or part crystalline. XRD works by irradiating a material with incident X-rays and then measuring the intensities and scattering angles of the X-rays that leave the material. The Definition of x-ray diffraction is.
The size of the obstacle should nearly be equal to the wavelength of light used. Definition of X-ray Diffraction XRD The wavelengths of X-rays are of the same order of magnitude as the distances between atoms or ions in a molecule or crystal 10 -10 m which equals 1 . Single-frame CDI in the X-ray region has potential use for probing dynamic phenomena with a high spatiotemporal resolution.
The science dealing with the study of crystals. X-ray powder diffraction XRD is a rapid analytical technique primarily used for phase identification of a crystalline material and can provide information on unit cell dimensions. A powder x-ray diffractometer in motion X-ray crystallography XRC is the experimental science determining the atomic and molecular structure of a crystal in which the crystalline structure causes a beam of incident X-rays to diffract into many specific directions.
Diffraction - when light passes sharp edges or goes through narrow slits the rays are deflected and produce fringes of light and dark bands. Prior to the discovery of X-ray diffraction in 1912 it was virtually impossible to prove that any microscopic grit produced contained diamond There was fair agreement between qualitative mineral content determined by X-ray diffraction and mineral content calculated from chemical results. The atomic planes of the crystal act on the X rays in exactly the same.
Glass rays indirect rays. The ionizing electromagnetic radiation emitted from a highly evacuated tube resulting from the excitation of the inner orbital electrons by the bombardment of the target anode with a stream of electrons from a heated cathode. X-ray diffraction a phenomenon in which the atoms of a crystal by virtue of their uniform spacing cause an interference pattern of the waves present in an incident beam of X rays.
It is a fact that for diffraction to occur. X-ray diffraction or XRD is a technique for analysing the atomic or molecular structure of materials. Coherent diffraction imaging CDI is a powerful method for visualizing the structure of an object with a high spatial resolution that exceeds the performance limits of the lens.
Ionizing electromagnetic radiation produced. X-ray like other electromagnetic rays can also be diffracted but for the diffraction of X-ray. Diffraction of light means the bending of light around the corner of an obstacle.
X-ray diffraction definition is - a scattering of X-rays by the atoms of a crystal that produces an interference effect so that the diffraction pattern gives information on the structure of the crystal or the identity of a crystalline substance. X-ray diffraction XRD is a commonly used technique for corrosion product analysis. Diffraction of x-rays by the regularly spaced atoms of a crystal useful for determining the arrangement of the atoms.
The diffraction pattern shows structure of the crystal. X-ray crystallography the determination of the three-dimensional structure of molecules by means of diffraction patterns produced by. Fundamental Principles of X-ray Powder Diffraction XRD.
Here we experimentally demonstrate a general method for single-frame X-ray CDI using a. X-Ray Diffraction XRD is a laboratory-based technique commonly used for identification of crystalline materials and analysis of unit cell dimensions. X-ray diffraction is a powerful nondestructive technique for characterizing crystalline materials.
It is the only technique for this type of analysis and it also. The analyzed material is finely ground homogenized and average bulk composition is determined. X-ray diffraction analysis XRD is a technique used in materials science to determine the crystallographic structure of a material.
One of two primary types of XRD analysis X-ray powder diffraction and single-crystal XRD is commonly applied to samples to obtain specific information about the crystalline material under investigation. The electrons in an atom coherently scatter light.
 X Ray Diffraction Xrd Rigaku Global Website
X Ray Diffraction Xrd Rigaku Global Website
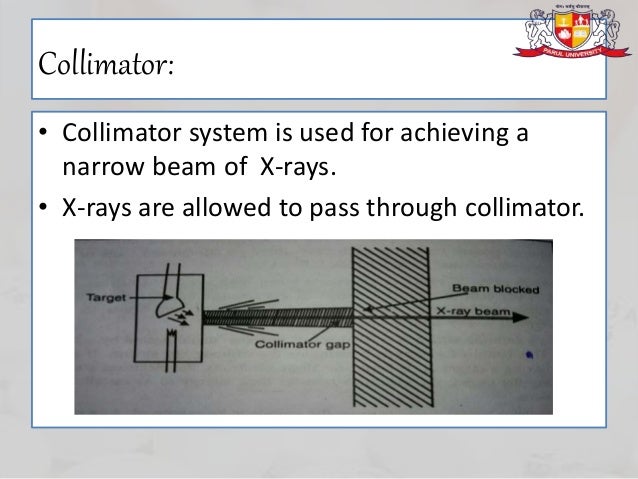 X Ray Diffraction And Applications
X Ray Diffraction And Applications
 X Ray Diffraction Qualitative And Quantitative Analysis
X Ray Diffraction Qualitative And Quantitative Analysis
 Determining Atomic Structures By X Ray Crystallography Introduction To Chemistry
Determining Atomic Structures By X Ray Crystallography Introduction To Chemistry
 Determination Of Crystal Structures By X Ray Diffraction X Ray Crystal Structure X Ray Tube
Determination Of Crystal Structures By X Ray Diffraction X Ray Crystal Structure X Ray Tube
 X Ray Crystallography 1 Ppt Video Online Download
X Ray Crystallography 1 Ppt Video Online Download
 100th Anniversary Of The Discovery Of X Ray Diffraction Chemviews Magazine Chemistryviews
100th Anniversary Of The Discovery Of X Ray Diffraction Chemviews Magazine Chemistryviews
 X Ray Crystallography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
X Ray Crystallography An Overview Sciencedirect Topics
 X Ray Diffraction Solid State Cbse Grade 12 Chemistry Youtube
X Ray Diffraction Solid State Cbse Grade 12 Chemistry Youtube
 X Ray Diffraction Xrd Anton Paar Wiki
X Ray Diffraction Xrd Anton Paar Wiki
 Rosalind Franklin And X Ray Diffraction Rosalind Franklin Born In July 25 1920 In London England Died April 16 1958 In London England Ovarian Cancer Ppt Download
Rosalind Franklin And X Ray Diffraction Rosalind Franklin Born In July 25 1920 In London England Died April 16 1958 In London England Ovarian Cancer Ppt Download
 X Ray Diffraction And Bragg Equation Youtube
X Ray Diffraction And Bragg Equation Youtube
 Ppt X Ray Diffraction Xrd Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4024666
Ppt X Ray Diffraction Xrd Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id 4024666






Post a Comment for "Definition Of X Ray Diffraction"